Making the Best of Vapor Recovery Systems
In oil and gas operations, it is important to eliminate the harmful vapors with toxic and explosive properties from gasoline and other fuels before selling the products. Vapor recovery is mainly crucial as hydrocarbon storing containers may be susceptible to leaks through the flaps and safety valves as the interior vapor pressure builds up.
What is Vapor Recovery?
Vapor recovery is the procedure of eliminating harmful fluid and vapor contaminants from basic products for improving purity and averting the release of poisonous contaminants. This process is also done in chemical processing sectors for recovering undesirable vapors from storing units for keeping the chemicals clean and safe for usage and transport.
Is Vapor Elimination Mandatory?
In different nations, vapor removal requirements are passed by environmental protection authorities, instructed by law, and binding on all operators and manufacturers involved in the dispensation and storing of natural gas, petroleum, and petrochemical products.
In the U.S., The EPA commands operators to perform vapor removal to control harmful emissions in natural gas plants, hydrocarbon storage services, and wells of natural gas under the Quad O.
Under this regulation, operators are required to eliminate a minimum of 95% of vapors formed in hydrocarbon storage units. The new standard places augmented requirements on oil and gas management for devising sustainable conduct to alleviate vapor pressure in tanks and avert costly emissions. One of the utmost competent systems for the removal of vapors is the vapor removal unit.
What Is a VRU?
A VRU is an arrangement designed for the removal of unwelcome vapors in crude oil or tanks letting operators obey emission regulations. VRU systems can be used in a number of chemical industries with quite a few variants accessible. For instance, a vapor recovery unit for storage tanks can be employed to recover gas from crude oil and concentrate tanks at storage amenities.
Working on a VRU
VRUs are automatically driven by a gas engine or an electric motor, whichever is available. The working of the VRU is based on the Ideal gas law. In essence, when you compress your process gas into a lesser volume, the gas pressure increases.
The characteristic VRU has four main components:
• Gas Compressor
• Scrubber
• Variable Frequency Drives
• Switching device
Working on a VRU
The main function of a VRU system is removing the vapors collected inside sealed hydrocarbon tanks. The mechanism does this by the compression of gas and suction.
The procedure of vapor recovery involves the subsequent steps:
• The gas compressor pulls liquid molecules into the scrubber
• The scrubber eliminates the water vapor, remains, and undesirable fluids from the tank.
• The recovered vapor is driven into gas lines and the liquids that are trapped are channeled to the pipes.
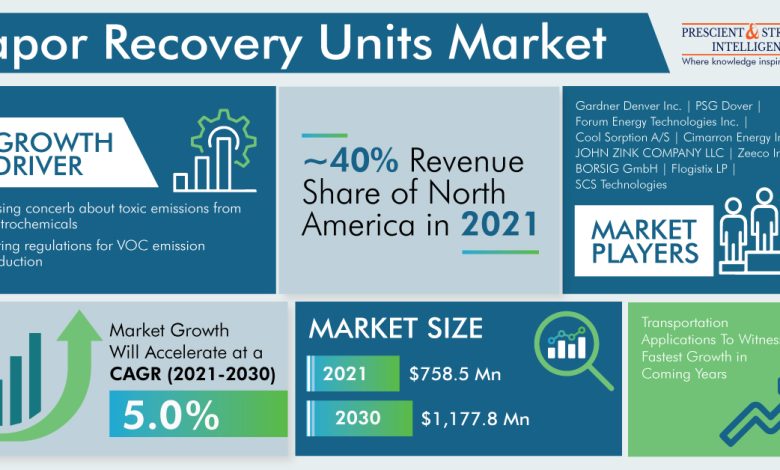
Due to the rising concerns regarding toxic emissions from pharmaceuticals, the demand for vapor recovery units is on the roll, and the value of same will be reaching a value of around $1,1778 million by the year 2030.
Read more: https://www.psmarketresearch.com/market-analysis/vapor-recovery-units-market